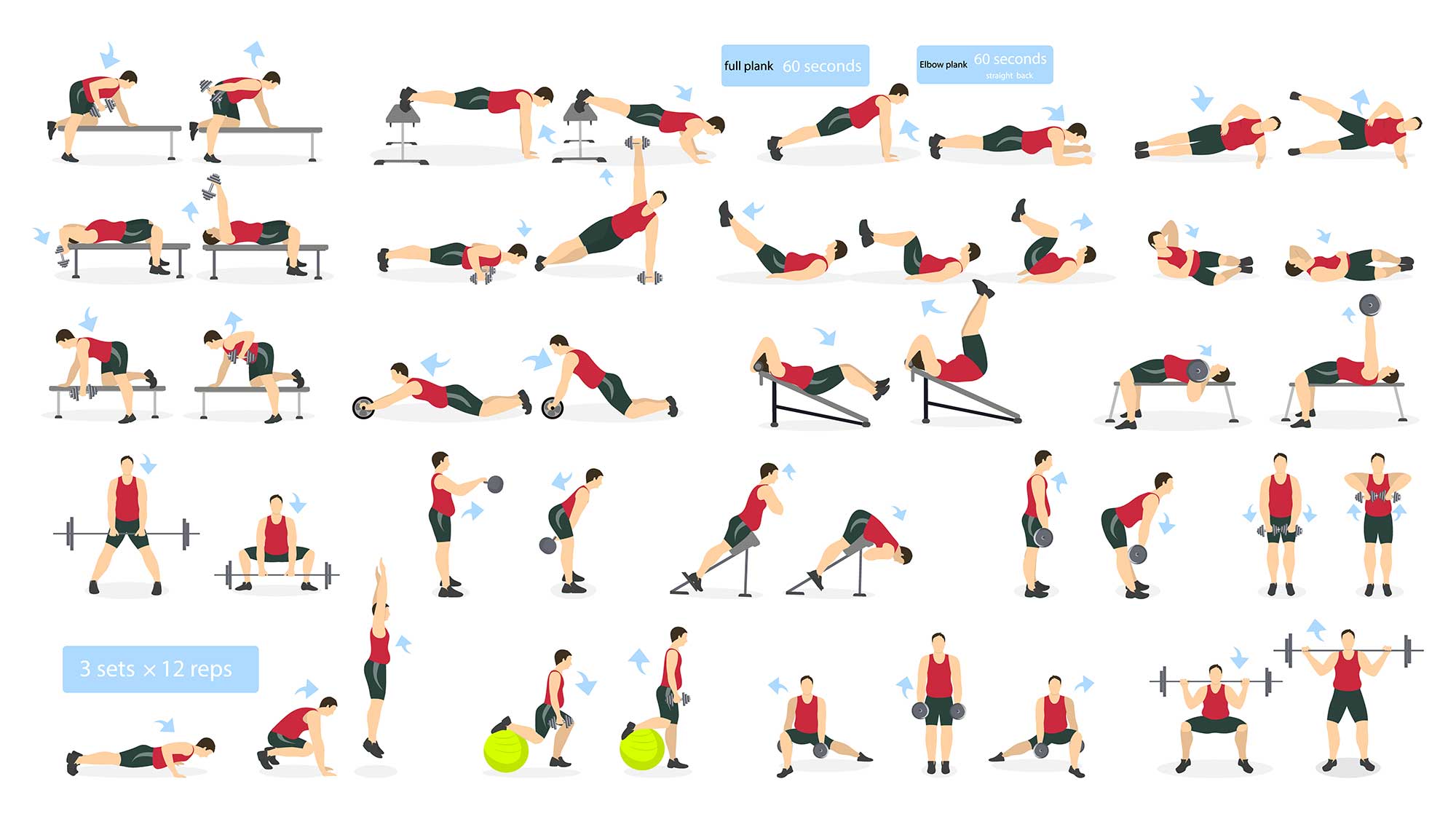
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to reaching fitness objectives. However, include full-body exercises in your regimen is one of the best tactics. These exercises work a variety of muscle groups and can be modified to meet different fitness objectives, such as weight loss, strength training, or endurance improvement.
The greatest full-body workouts, efficient exercises, and how to design a workout regimen that will help you reach your fitness objectives will all be covered in this article.
Full-Body Workouts: What Are They?
Advantages of Whole-Body Exercise
- Efficiency: Save time by training every muscle group in a single session.
- Caloric Burn: To raise your heart rate and speed up your metabolism, use many muscles at once.
- Balanced Strength: Prevent muscular imbalances and encourage balanced muscle growth.
- Variety: To keep workouts lively and captivating, mix up the routines.
- Adaptability: Fits a range of fitness levels and permits adjustments and advancements.
The Greatest Whole-Body Exercises
The top full-body exercises that can assist you in reaching your fitness objectives are listed below:
1. Training on Circuits
Strength training and aerobic exercises are combined in circuit training, which makes it a powerful tool for fat burning and muscle growth. Exercises like jumping jacks, squats, and push-ups could be included in a standard circuit.
Circuit Example:
| Exercise | Duration/Repeats |
|---|---|
| Push-ups | 12-15 reps |
| Squats | 12-15 reps |
| Dumbbell Rows | 12-15 reps |
| Plank | 30 seconds |
| Burpees | 30 seconds |
2. High-Intensity Interval Training, or HIIT,
The capacity of HIIT to burn calories quickly is well-known. You may increase your strength and cardiovascular fitness by switching between high-intensity workouts and low-intensity rest.HIIT Workout Example:
| Exercise | Duration |
|---|---|
| Sprint | 30 seconds |
| Rest | 30 seconds |
| Jump Squats | 30 seconds |
| Rest | 30 seconds |
| Mountain Climbers | 30 seconds |
| Rest | 30 seconds |
3. Exercises Using Your Bodyweight
Everyone can perform bodyweight exercises because they don't require any special equipment and can be done anyplace. All of the main muscle groups may be efficiently targeted by them.Bodyweight Exercises That Work:
- Lunges
- Squats
- Push-ups
- Variations of planks
- Burpees
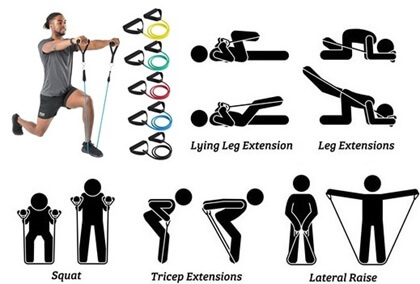
4. Training with Resistance
Resistance Training Advantages
- Muscle Strength and Hypertrophy: Resistance exercise causes muscular fibers to be stimulated, which results in muscle development. Stronger muscles improve physical performance overall, simplifying daily chores and enhancing athletic ability.
- Bone Density: Regular resistance exercise lowers the risk of osteoporosis and enhances bone density, especially in older persons. Weight-bearing activities put mechanical stress on bones, which promotes bone mineralization and development.
- Metabolic Rate: Because muscle tissue is metabolically active, an individual's resting metabolic rate (RMR) increases with muscle mass. Since more calories are expended even when at rest, this can help with weight control and fat loss.
- Functional Strength: Resistance exercise increases functional strength, which leads to better performance in everyday tasks like hauling, lifting, and stair climbing. Because it can lower the risk of falls and accidents, this is particularly crucial for senior citizens.
- Mental Health: Frequent resistance training has been associated with better mental health outcomes, such as less signs of sadness and anxiety. Exercise causes endorphins to be released, which can improve mood and foster a sense of wellbeing.
- Injury Prevention: Resistance exercise can help prevent injuries by fortifying the muscles, tendons, and ligaments around joints. Better overall joint function and a lower incidence of musculoskeletal injuries are two benefits of increased muscle stability and balance.
Resistance Training Types
- First, the free weights: Free weight exercises, such those with dumbbells, barbells, or kettlebells, include several muscular groups and call for stability. Squats, deadlifts, and bench presses are a few examples.
- Weight Machines: Resistance machines are appropriate for novices and anyone recuperating from injuries since they direct movement and offer a predetermined course. They make it possible to exercise certain muscles with varying degrees of resistance.
- Body-Weight Exercises: These exercises use the weight of the person performing them as resistance. Lunges, squats, push-ups, and pull-ups are typical examples. They frequently don't require any equipment and may be performed anyplace.
- Bands of Resistance: Resistance bands are portable, adaptable, and provide varied resistance. They may be used to a variety of workouts that focus on various muscle groups. They are very helpful for mobility training and rehabilitation.
- Training for Functions: This method improves strength and coordination by using exercises that resemble daily tasks. To improve general functional fitness, it frequently combines a variety of resistance training techniques.
Establishing a Program for Resistance Training
1. Rates
Aim for two to three workouts a week at the very least, giving your muscles enough time to rest and heal in between.
2. Intensity
The level of difficulty should be moderate to ensure perfect form while still being difficult enough to encourage strength growth. Apply the idea of "progressive overload," increasing resistance or weights progressively as strength increases.
3. Volume
The overall quantity of work completed (sets x reps) is referred to as volume. For muscular hypertrophy, 3–4 sets of 8–12 repetitions or 4-6 sets of 4-6 repetitions are popular methods.
4. Intervals of Rest
Depending on the exercise's intensity and your training objectives, allow for rest periods in between sets, which typically last between 30 and 2 minutes.
5. Diversity
To avoid plateaus and sustain interest, change up your workouts to target various muscle groups and movement patterns.
6. Cheal Down and Warm Up
Always start with a appropriate warm-up to get the joints and muscles ready for exercise, followed by a cool-down to promote flexibility and recuperation.
Depending on the exercise's intensity and your training objectives, allow for rest periods in between sets, which typically last between 30 and 2 minutes.
5. Diversity
To avoid plateaus and sustain interest, change up your workouts to target various muscle groups and movement patterns.
6. Cheal Down and Warm Up
Always start with a appropriate warm-up to get the joints and muscles ready for exercise, followed by a cool-down to promote flexibility and recuperation.
A complete and accurate fitness program should include resistance training as it has many positive effects on both physical and mental health. People can increase their strength, body composition, metabolic rate, and general well-being by regularly participating in resistance exercise. Including weight training in a fitness regimen can have major long-term advantages for athletes of all skill levels.
Strength training may be improved by including weights or resistance bands in your exercises. You can engage in a variety of activities that target distinct muscle groups.
An example of a resistance training regimen:
| Exercise | Sets | Reps |
|---|---|---|
| Deadlifts | 30 seconds | 8-10 |
| Bench Press | 30 seconds | 8-10 |
| Bent-over Rows | 30 seconds | 8-10 |
| Overhead Press | 30 seconds | 8-10 |
"Starting is the key to achieving success." Mark Twain(alert-success)
Establishing Your Whole-Body Exercise Program
Establish Your Objectives: What do you want to accomplish? Establish your goals, whether they be to lose weight, build muscle, or improve your general fitness.
Select Your Workouts: Choose a combination of isolation exercises, which focus on a single muscle, and complex motions, which engage many muscle groups.
Make a schedule: Choose the number of days a week that you can dedicate to exercising. Two to three days of full-body exercises could be plenty for novices.
Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Make sure you always incorporate a suitable warm-up to get your muscles warmed up and a cool-down to help you recuperate.
FAQs Regarding Whole-Body Exercises
1. How frequently should I work out my entire body?2-3 times a week is the best frequency for most people. This preserves frequency while enabling recovery.
2. Can novices perform full-body exercises?
Of course! Beginners benefit greatly from full-body workouts since they may begin with bodyweight exercises and work their way up to more difficult ones.
3. Do full-body exercises require any special equipment?
Not always. You don't need any special equipment to do good bodyweight workouts. But adding resistance bands or weights might make it more intense.
4. What is the ideal duration for a full-body workout?
Depending on the quantity and level of workouts, aim for 30 to 60 minutes.
5. Will working out my entire body aid in weight loss?
Indeed! Full-body exercises are good for losing weight since they may burn a lot of calories, especially when paired with cardio exercises.










I like this interesting
ReplyDeleteThanks
Delete