Decentralization
Overview
The idea of decentralization is causing a significant upheaval in the financial industry. Decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology are posing a threat to traditional financial systems, which have historically been dominated by centralized organizations like banks, governments, and financial intermediaries. The goal of these developments is to make the financial system more accessible, transparent, and open. We will examine the advantages, disadvantages, and prospects of this revolutionary movement as we examine the effects of decentralization on global finance in this blog.Going to understand Financial Decentralization
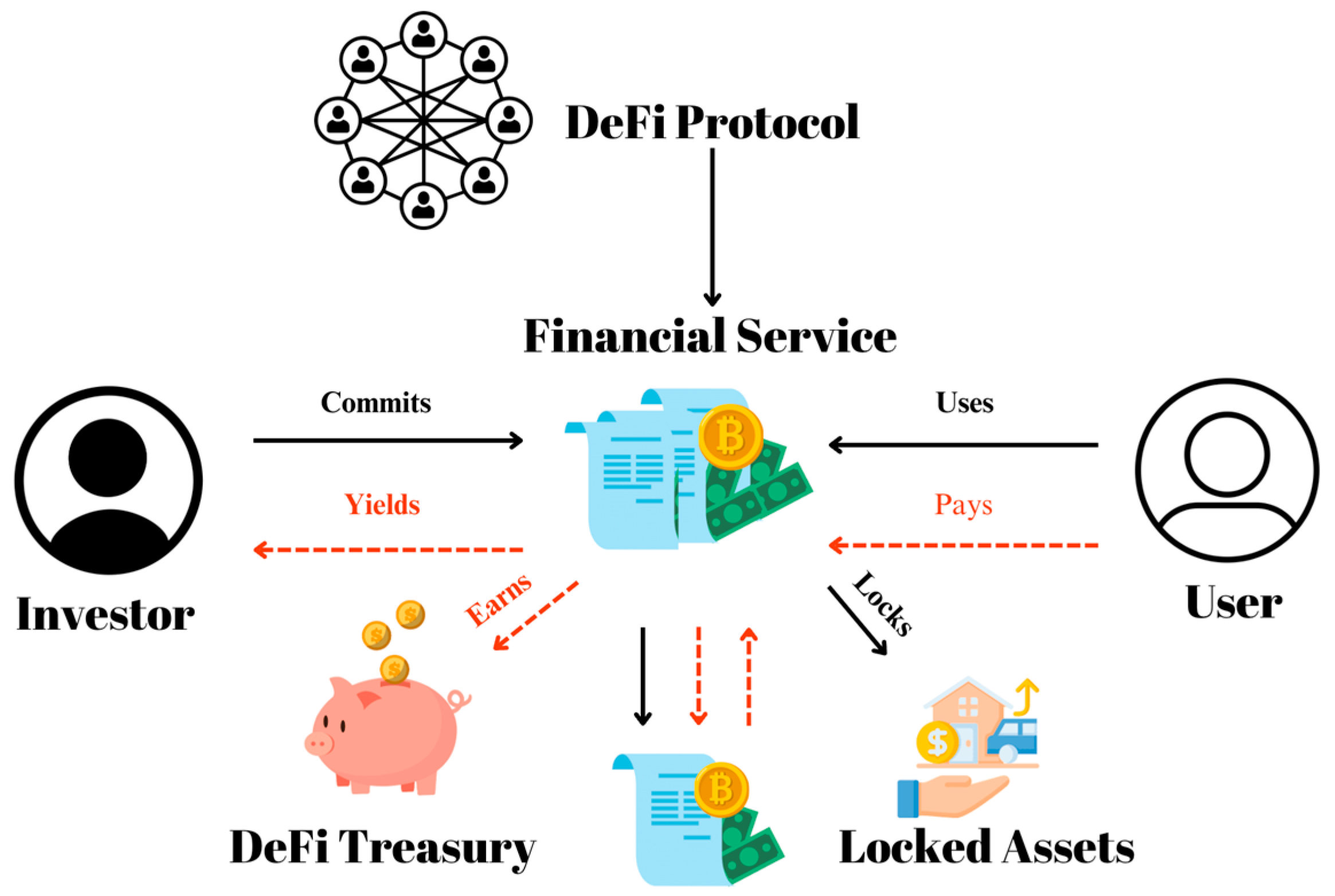
Fundamentally, decentralized finance (DeFi) uses blockchain networks such as Ethereum and Bitcoin to offer an alternative to traditional banking. Without depending on banks or other financial institutions, users may lend, borrow, trade, and earn interest on digital assets using DeFi platforms.
Principal Advantages of Financial Decentralization
1. Inclusion of Finances
Decentralization's capacity to offer financial services to underbanked and unbanked communities is among its most important benefits. Because of the stringent documentation, credit history, and geographic requirements of traditional banking institutions, millions of people are unable to participate in the financial system. In contrast, DeFi systems allow users to access financial services with just a digital wallet and an internet connection.2. Openness and Safety
Blockchain technology makes guarantee that every transaction is visible and unchangeable by recording it on a public ledger. Decentralized finance uses open-source protocols, which enable anybody to examine transactions and confirm their validity, in contrast to traditional financial organizations where decisions are frequently made behind closed doors.3. More Efficiency and Reduced Expenses
Decentralized finance boosts efficiency and lowers transaction costs by doing away with middlemen. Conventional banks levy exorbitant costs for money transfers, loan processing, and cross-border transactions. DeFi facilitates direct user-to-user transactions with negligible costs and almost immediate processing times.4. Resistance to Control and Censorship
Because decentralized networks don't have a single point of failure, they are more resistant to censorship, economic downturns, and governmental control. Decentralized finance guarantees that users have complete control over their assets, as contrast to traditional banks that have the authority to halt transactions or freeze accounts.The Difficulties of Financial Decentralization
1. Uncertainty in regulations
Regulating decentralized finance continues to be a challenge for governments and financial authorities worldwide. DeFi systems can be exposed to legal concerns and uncertainties in the absence of clear laws, which might impede their expansion and use.2. Problems with Scalability
Transaction speeds and network congestion are two of the main scalability issues that blockchain networks are now facing. Solutions like layer-2 scalability, sharding, and improved consensus techniques will be required to accommodate a greater user population as DeFi use increases.3. Hacks and Security Risks
Decentralized platforms are susceptible to security threats even though they are more open. Fraudulent initiatives, hacking events, and smart contract weaknesses have resulted in large financial losses. To reduce dangers, users should thoroughly investigate DeFi initiatives before funding them.Decentralized Finance's Future
The future of finance will be greatly influenced by innovations like decentralized identification solutions, blockchain network interoperability, and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs).
Furthermore, trading tactics, risk assessments, and fraud detection may be further optimized by integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning inside DeFi protocols. DeFi will become more effective and accessible with the creation of cross-chain solutions and scalability enhancements, which will also speed up transactions and lower expenses.
Education and awareness campaigns will be crucial in assisting people in comprehending the advantages and dangers of decentralized money as user acceptance increases. Programs for financial literacy that emphasize blockchain and DeFi applications can help close the gap between those who utilize traditional money and those who live in a decentralized society.
In the end, decentralized finance's success will rely on technology developments, broad acceptance, and clear regulations. If these issues are successfully resolved, DeFi may be able to reshape the world financial system and create a more open, transparent, and a productive economy for coming generations.
Education and awareness campaigns will be crucial in assisting people in comprehending the advantages and dangers of decentralized money as user acceptance increases. Programs for financial literacy that emphasize blockchain and DeFi applications can help close the gap between those who utilize traditional money and those who live in a decentralized society.
In the end, decentralized finance's success will rely on technology developments, broad acceptance, and clear regulations. If these issues are successfully resolved, DeFi may be able to reshape the world financial system and create a more open, transparent, and a productive economy for coming generations.
Table of Comparisons between Decentralized and Conventional Finance
| Feature | Traditional Finance | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Centralized (banks, governments) | Decentralized (blockchain, smart contracts) |
| Accessibility | Requires documentation, location-based | Global access via the internet |
| Transparency | Limited, controlled by institutions | Fully transparent and publicly auditable |
| Innovation | Slow to adopt new technologies | Rapid innovation and growth |
| Transaction Speed | Slow, especially for cross-border transfers | Fast, near-instant transactions |
| Cost Efficiency | High fees for transfers and services | Low fees due to removal of intermediaries |
| Security | Susceptible to fraud, data breaches | More secure but vulnerable to smart contract risks |
| Regulation | Well-established, highly regulated | Uncertain, evolving regulatory framework |
FAQ
1. What is DeFi, or decentralized finance?Financial services that run on blockchain networks without the need of middlemen like banks are referred to as decentralized finance (DeFi). Smart contracts allow users to trade, lend, borrow, and invest.
2. How is security ensured by DeFi?
DeFi uses blockchain technology, which offers immutability and transparency. But there are still security issues, such hacker threats and smart contract weaknesses. Before making an investment, users should perform due diligence.
3. Does DeFi have regulations?
DeFi regulations differ from nation to nation and are constantly changing. Frameworks for integrating DeFi into the larger financial system under supervision are being developed by certain countries.
4. Is DeFi accessible?
Yes, anyone with a digital wallet and an internet connection can use DeFi. It is more inclusive since it doesn't require the infrastructure of traditional banking.
5. What dangers does DeFi pose?
Risks include possible fraud, regulatory uncertainties, smart contract faults, and volatility. Before investing, investors should exercise caution and do extensive research on enterprises.
In ending
Decentralization is transforming the banking sector by increasing security, efficiency, and accessibility. Even if there are still obstacles to overcome, decentralized finance has the potential to build an open and equitable financial system. The way we deal with money and financial services may change as decentralized finance emerges as the next global paradigm as blockchain technology develops and regulatory clarity increases.Businesses and people may take part in a more robust, inclusive, and transparent financial system by adopting decentralization. The global economy will surely be shaped for years to come by the influence of the recent beginnings of the shift to a decentralized financial future.